A course by MoMA and Coursera
Art period
An art period is a phase in the development of the work of an artist, a group or art movement, from Wikipedia
Renaissance
1300 - 1602Renaissance to Neoclassicism (新古典主义)
1520 - 1830Romanticism
1979 - 1880Romanticism to Modern Art
1803 - 1854Modern Art
1860 - 1945Contemporary art
1946 - present
Modern Art timeline
IMPRESSIONISM
(C.1870-1890)POST IMPRESSIONISM
(C.1885-1905)FAUVISM
(1905-1910)GERMAN EXPRESSIONISM
(1905-1925)ABSTRACT ART
(C.1907 ONWARDS)CUBISM
(1907-1915)FUTURISM
(1909-1914)SUPREMATISM
(C.1915-1925)CONSTRUCTIVISM
(C.1913-1930)DE STIJL
(C.1917-1931)
IMPRESSIONISM (C.1870-1890)
a colorful style of painting in France
searched for a more exact analysis of the effects of color and light in nature.
capture the atmosphere of a particular time of day (or different weather)
 CLAUDE MONET (1840-1926) 'Rouen Cathedral in Full Sunlight', 1893-94 (oil on canvas)
CLAUDE MONET (1840-1926) 'Rouen Cathedral in Full Sunlight', 1893-94 (oil on canvas)
Artists
Claude Monet, Pierre Auguste Renoir 雷诺阿, Edgar Degas 德加, Camille Pissarro 毕沙罗, Alfred Sisley 西斯莱, Henri de Toulouse Lautrec 罗特列克
POST IMPRESSIONISM (C.1885-1905)
not a particular style, but a collective title given to a few artists
developed a range of personal styles, influenced the development of art in the 20th century
 VINCENT VAN GOGH (1853-90)
'Café Terrace at Night', 1888 (oil on canvas)
VINCENT VAN GOGH (1853-90)
'Café Terrace at Night', 1888 (oil on canvas)
Cézanne was an important influence on Picasso and Braque in their development of Cubism.
Van Gogh’s vigorous and vibrant painting technique was one of the touchstones of both Fauvism and Expressionism
Gauguin’s symbolic color and Seurat’s pointillist technique were an inspiration to ‘Les Fauves’ 野兽派.
 Paul Cézanne, Apples and Oranges (1899)
Paul Cézanne, Apples and Oranges (1899)
Artists
Paul Cézanne 塞尚, Paul Gauguin 高更, Vincent Van Gogh, Georges Seurat 修拉
FAUVISM 野兽派 (1905-1910)
Developed in France at the beginning of the 20th century by Henri Matisse, André Derain
joyful style of painting that delighted in using outrageously bold colors, color be used at its highest pitch to express the artist’s feelings (rather than describe what it looks like)
- extremely simplified drawing
- intensely exaggerated color
- a major influence on German Expressionism
 HENRI MATISSE (1869-1954)
'The Open Window, Collioure', 1905 (oil on canvas)
HENRI MATISSE (1869-1954)
'The Open Window, Collioure', 1905 (oil on canvas)
Artists
Henri Matisse 马蒂斯, André Derain 德兰
GERMAN EXPRESSIONISM 德国表现主义 (1905-1925)
an emotional or spiritual vision of the world
inspiration from Vincent Van Gogh and Edvard Munch, also German Gothic and ‘primitive art’
 ERNST LUDWIG KIRCHNER (1880-1938) 'The Red Tower at Halle', 1915 (oil on canvas)
ERNST LUDWIG KIRCHNER (1880-1938) 'The Red Tower at Halle', 1915 (oil on canvas)
Artists
Die Brücke, Der Blaue Reiter
ABSTRACT ART (C.1907 ONWARDS)
withdraw part of something in order to consider it separately (‘something’ = visual elements of a subject: its line, shape, tone, pattern, texture, form)
Semi-Abstraction is where the image still has one foot in representational art, (see Cubism and Futurism).
selects, develops and refines specific visual elements (e.g. line, color and shape), to create a poetic reconstruction or simplified essence of the original subject
Pure Abstraction is where the artist uses visual elements independently as the actual subject of the work itself. (see Suprematism, De Stijl and Minimalism).
the roots of modern abstract art are to be found in Cubism
 GEORGES BRAQUE (1882-1963) 'Violin and Pitcher', 1910 (oil on canvas)
GEORGES BRAQUE (1882-1963) 'Violin and Pitcher', 1910 (oil on canvas)
Artists
Concluded below.
CUBISM 立体主义 (1907-1915)
invented around 1907 in Paris by Pablo Picasso and Georges Braque. It was the first abstract style of modern art.
ignore the traditions of perspective drawing and show you many views of a subject at one time
they drew on the expressive energy of art from other cultures, particularly African art
two phases: Analytical Cubism (pre-1912) and Synthetic Cubism (post-1912).
 PABLO PICASSO (1881-1973) 'Ambroise Vollard 一个人名', 1915 (oil on canvas)
PABLO PICASSO (1881-1973) 'Ambroise Vollard 一个人名', 1915 (oil on canvas)
Artists
Pablo Picasso, Georges Braque 布拉克, Juan Gris, Fernand Leger, Robert Delaunay, Albert Gleizes, Jean Metzinger, Louis Marcoussis, Marie Laurencin
FUTURISM (1909-1914)
revolutionary Italian movement that celebrate modernity, attacked the long tradition of Italian art in favour of a new avant-garde 先锋派
They glorified industrialization, technology, and transport along with the speed, noise and energy of urban life.
adopted the visual vocabulary of Cubism to express their ideas - but appear more dynamic
 GIACOMO BALLA (1871-1959) 'The Rhythm of the Violinist', 1912 (oil on canvas)
GIACOMO BALLA (1871-1959) 'The Rhythm of the Violinist', 1912 (oil on canvas)
Artists
Filippo Tommaso Marinetti 马里内蒂, Umberto Boccioni, Giacomo Balla, Gino Severini, the musician Luigi Russolo, the architect Antonio Sant’Elia
SUPREMATISM 至上主义 (C.1915-1925)
developed in 1915 by the Russian artist Kazimir Malevich
geometric style of abstract painting derived from elements of Cubism and Futurism
Malevich rejected any use of representational images, believing that the non-representational forms of pure abstraction had a greater spiritual power
Suprematism: pure abstraction that advocated a mystical approach to art
Constructivism (the major Russian art movement of the 20th Century): served the social and political ideology of the state
 KAZIMIR MALEVICH (1879-1935) 'Suprematism', 1915 (oil on canvas)
KAZIMIR MALEVICH (1879-1935) 'Suprematism', 1915 (oil on canvas)
Artists
Kazimir Malevich 卡济米尔·马列维奇
CONSTRUCTIVISM 构成主义 (C.1913-1930)
same geometric language as Suprematism
abandoned its mystical vision in favour of their ‘Socialism of vision‘ - a Utopian glimpse of a mechanized modernity according to the ideals of the October Revolution (1917)
However, it’s eventually repressed and replaced by Socialist Realism
 EL LISSITZKY (1890-1941) 'The Red Wedge', 1919 (lithograph)
EL LISSITZKY (1890-1941) 'The Red Wedge', 1919 (lithograph)
Artists
Vladimir Tatlin 塔特林, Alexander Rodchenko, El Lissitzky 利西茨基 and Naum Gabo
DE STIJL 风格主义 (C.1917-1931)
a Dutch ‘style’ of pure abstraction
Mondrian was a deeply spiritual man who was intent on developing a universal visual language that was free from any hint of nationalism that led to the Great War.
refined the elements to a grid of lines and primary colors (a series of compositions that explored his universal principles of harmony)
Vertical lines embodied the direction and energy of the sun’s rays, countered by horizontal lines relating to the earth’s movement around it
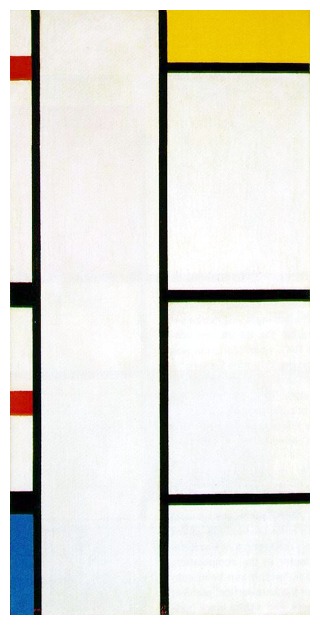 PIET MONDRIAN (1872-1944) 'Composition with White and Yellow', 1942 (oil on canvas)
PIET MONDRIAN (1872-1944) 'Composition with White and Yellow', 1942 (oil on canvas)
Artists
Piet Mondrian 蒙德里安, Theo Van Doesburg, Bart van der Leck
Reference
http://www.artyfactory.com/art_appreciation/timelines/modern_art_timeline.htm